k = gaussian([2, 0.1], size = int(1e5), bound = [0, 2])
plt.hist(k, bins = 200);
utils_trajectoriespert (params:list, size:int=1, lamb=4)
Samples from a Pert distribution of given parameters
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| params | list | Pert parameters a, b, c | |
| size | int | 1 | number of samples to get |
| lamb | int | 4 | lambda pert parameters |
| Returns | array | samples from the given Pert distribution |
gaussian (params:list|int, size=1, bound=None)
Samples from a Gaussian distribution of given parameters.
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| params | list | int | If list, mu and sigma^2 of the gaussian. If int, we consider sigma = 0 | |
| size | int | 1 | Number of samples to get. |
| bound | NoneType | None | Bound of the Gaussian, if any. |
| Returns | array | Samples from the given Gaussian distribution |
sample_sphere (N:int, R:int|list)
Samples random number that lay in the surface of a 3D sphere centered in zero and with radius R.
| Type | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| N | int | Number of points to generate. |
| R | int | list | Radius of the sphere. If int, all points have the same radius, if numpy.array, each number has different radius. |
| Returns | array | Sampled numbers |
bm1D (T:int, D:float, deltaT=False)
Creates a 1D Brownian motion trajectory
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| T | int | Length of the trajecgory | |
| D | float | Diffusion coefficient | |
| deltaT | bool | False | Sampling time |
| Returns | array | Brownian motion trajectory |
regularize (positions:<built-infunctionarray>, times:<built- infunctionarray>, T:int)
Regularizes a trajectory with irregular sampling times.
| Type | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| positions | array | Positions of the trajectory to regularize |
| times | array | Times at which previous positions were recorded |
| T | int | Length of the output trajectory |
| Returns | array | Regularized trajectory. |
normalize (trajs)
Normalizes trajectories by substracting average and dividing by SQRT of their standard deviation.
| Type | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| trajs | np.array | Array of length N x T or just T containing the ensemble or single trajectory to normalize. |
normalize_fGN (disp, alpha, D, T:int, deltaT:int=1)
Normalizes fractional Gaussian Noise created with stochastic library.
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| disp | Array-like of shape N x T or just T containing the displacements to normalize. | ||
| alpha | float in [0,2] or array-like of length N x 1 | Anomalous exponent | |
| D | float or array-like of shape N x 1 | Diffusion coefficient | |
| T | int | Number of timesteps the displacements were generated with | |
| deltaT | int | 1 | Sampling time |
| Returns | Array-like containing T displacements of given parameters |
N = 10; T = 10
trajs = 3*np.random.randn(N*T*2).reshape(N,T,2)
trajs = np.cumsum(trajs, axis = 1)
norm_trajs = normalize(trajs)
idx = 0; plt.figure(figsize = (3,3))
plt.plot(trajs[idx,:,0]-trajs[idx,0,0], '-o', label = 'Original trajectory')
plt.plot(norm_trajs[idx,:,0], '-o', label = 'Normalized')
plt.legend(); plt.xlabel('Time'); plt.ylabel('Position')Text(0, 0.5, 'Position')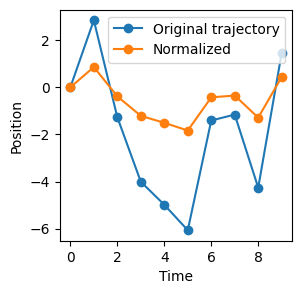
Needed for the correct calculation of confined diffusion in circular compartments.
trigo ()
This class gathers multiple useful trigonometric relations.
Inspired from: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/30844482/what-is-most-efficient-way-to-find-the-intersection-of-a-line-and-a-circle-in-py and http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Circle-LineIntersection.html
trigo.circle_line_segment_intersection (circle_center, circle_radius, pt1, pt2, full_line=False, tangent_tol=1e-09)
Find the points at which a circle intersects a line-segment. This can happen at 0, 1, or 2 points.
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| circle_center | tuple | The (x, y) location of the circle center | |
| circle_radius | float | The radius of the circle | |
| pt1 | tuple | The (x, y) location of the first point of the segment | |
| pt2 | tuple | The (x, y) location of the second point of the segment | |
| full_line | bool | False | True to find intersections along full line - not just in the segment. False will just return intersections within the segment. |
| tangent_tol | float | 1e-09 | Numerical tolerance at which we decide the intersections are close enough to consider it a tangent |
| Returns | Sequence[Tuple[float, float]] | A list of length 0, 1, or 2, where each element is a point at which the circle intercepts a line segment. |
find_nan_segments (a, cutoff_length)
Extract all segments of nans bigger than the set cutoff_length. If no segments are found, returns None. For each segments, returns the begining and end index of it.
Output: array of size (number of segments) x 2.
segs_inside_fov (traj, fov_origin, fov_length, cutoff_length)
Given a trajectory, finds the segments inside the field of view (FOV).
| Type | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| traj | array | Set of trajectories of size N x T (N: number trajectories, T: length). |
| fov_origin | tuple | Bottom right point of the square defining the FOV. |
| fov_length | float | Size of the box defining the FOV. |
| cutoff_length | float | Minimum length of a trajectory inside the FOV to be considered in the output dataset. |
| Returns | array | Set of segments inside the FOV. |
inside_fov_dataset (trajs, labels, fov_origin, fov_length, cutoff_length=10, func_labels=None, return_frames=False)
Given a dataset of trajectories with labels and a FOV parameters, returns a list of trajectories with the corresponding labels inside the FOV
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| trajs | array | Set of trajectories with shape T x N x 2. | |
| labels | array | Set of labels with shape T x N x 2. | |
| fov_origin | tuple | Bottom left point of the square defining the FOV. | |
| fov_length | float | Size of the box defining the FOV. | |
| cutoff_length | int | 10 | Minimum length of a trajectory inside the FOV to be considered in the output dataset. |
| func_labels | NoneType | None | (optional) Function to be applied to the labels to take advantage of the loop. |
| return_frames | bool | False | |
| Returns | tuple | - trajs_fov (list): list 2D arrays containing the trajectories inside the field of view. - labels_fov (list): corresponding labels of the trajectories. |
Example: (check notebooks for full details)
fig, (ax, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize = (14,7))
colors = plt.cm.RdYlGn(np.linspace(0, 1, len(trajs_fov)))
for idx, og_traj in enumerate(trajs[:, :, :].transpose(1,0,2)):
ax.plot(og_traj[:, 0], og_traj[:, 1], c = 'k', alpha = 0.5, lw = 0.8)
for t, c in zip(trajs_fov, colors[::-1, :]):
ax.plot(t[0], t[1], c= c)
ax2.scatter(t[0], t[1], facecolor = c, s = 1)
# FOV
fov_min_x, fov_min_y = fov_origin
fov_max_x, fov_max_y = np.array(fov_origin)+fov_length
# currentAxis = ax.gca()
ax.add_patch(Rectangle((fov_min_x, fov_min_y), fov_length, fov_length, fill=None, alpha=1, lw = 2, label = 'FOV'))
# Boundary
ax.axhline(0, alpha = 0.5, ls = '--', c = 'k', label = 'boundary')
ax.axhline(L, alpha = 0.5, ls = '--', c = 'k')
ax.axvline(0, alpha = 0.5, ls = '--', c = 'k')
ax.axvline(L, alpha = 0.5, ls = '--', c = 'k')
# FOV origin
ax.scatter(fov_origin[0], fov_origin[1], label = 'FOV origin', s = 40, zorder = 10)
legend = ax.legend()
legend.get_frame().set_alpha(None)
plt.setp(ax, xlabel = 'X (px)', ylabel = 'Y (px)')
plt.setp(ax2, xlim = (0,L), ylim = (0,L));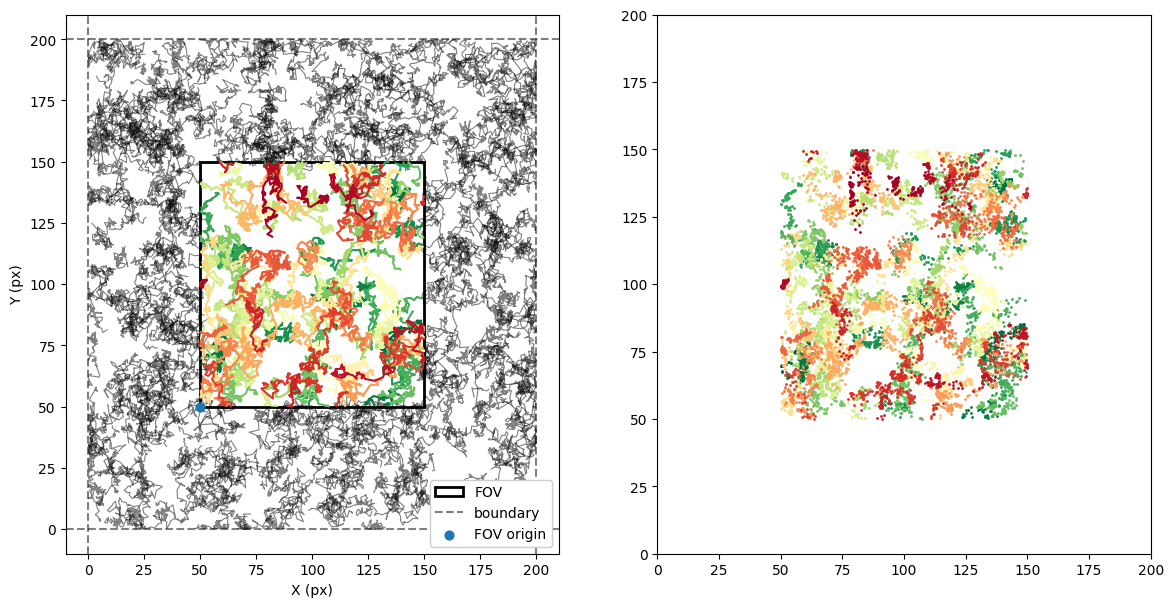
motion_blur (output_length:int, oversamp_factor:float=10, exposure_time:float=0.5)
Applies a motion blur to given trajectories. Motion blur is apply by considering an oversampled trajectory and then averaging the position over the exposure time. The oversampling is controled by the oversampling factor O.
If we want to generate trajectories of size T, we must input trajectories of size T*O. The trajectory is then reshape into chunks of size O. The output position for each chunk is the average over the exposure time, i.e. the percentage of the beginning of this chunk.
| Type | Default | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|
| output_length | int | Expected length of trajectories after applying motion blur | |
| oversamp_factor | float | 10 | Oversampling factor. This implies that the number of frames goes from input -> T*O to output -> T |
| exposure_time | float | 0.5 | Percentage of the oversampled (i.e in [0,1]) |
motion_blur.apply (trajs:<built-infunctionarray>)
Applies the motion blur with the parameters defined.
| Type | Details | |
|---|---|---|
| trajs | array | Input trajectories. Must be of size (input_length, num_trajs, dimension) |
| Returns | array | Output trajectories after applying motion blur. Size: (input_length / oversamp_factor, num_trajs, dimension) |
Example:
MB = motion_blur(output_length = 10, oversamp_factor = 10, exposure_time = 0.5)
trajs = np.random.randn(100, 5, 2).cumsum(0)
trajs[:,0,0] = np.arange(100) # we put a straight line to check what happens
mb_trajs = MB.apply(trajs)
_, axs = plt.subplots(2,5,figsize = (15,6))
for t, t_mb, ax in zip(trajs.transpose(1,0,2), mb_trajs.transpose(1,0,2), axs.transpose()):
ax[0].plot(np.linspace(0,10,t.shape[0]), t[:,0], label = 'OG traj')
ax[0].plot(np.linspace(0,10,t_mb.shape[0]), t_mb[:,0], 'o-', alpha = 0.8, label = 'motion blur')
ax[1].plot(np.linspace(0,10,t.shape[0]), t[:,1])
ax[1].plot(np.linspace(0,10,t_mb.shape[0]), t_mb[:,1], 'o-', alpha = 0.8)
axs[0,0].legend()
plt.setp(axs, yticklabels = []);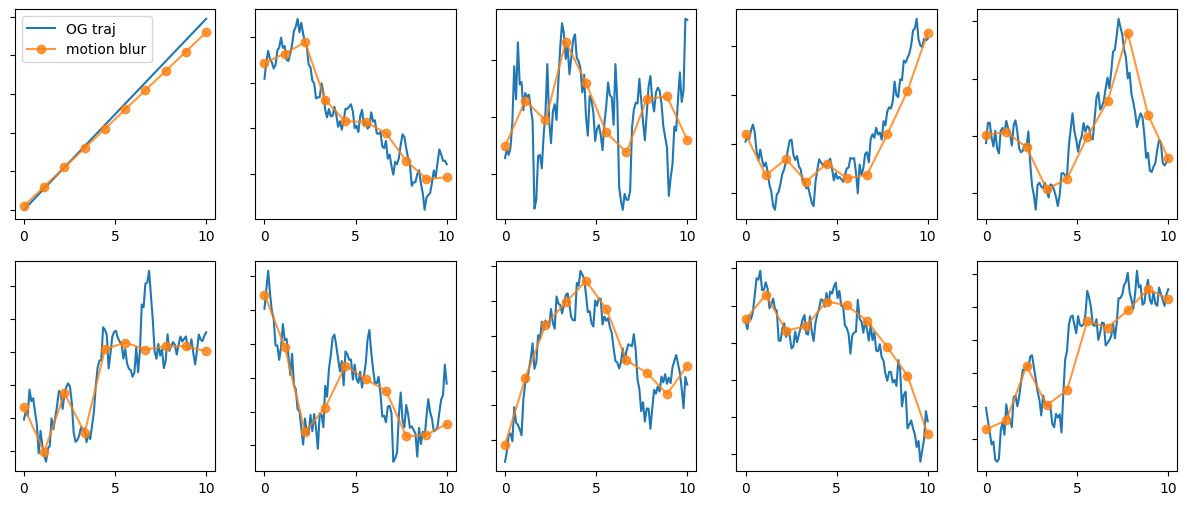
plot_trajs (trajs, L, N, num_to_plot=3, labels=None, plot_labels=False, traps_positions=None, traps_r=None, comp_center=None, r_cercle=None)